Sprache: DE
What does the Battery Act (BattG) Germany regulate?

1. Introduction to the BattG in Germany
1.1 Definition and Objective of the BattG
The Battery Act (BattG) of the Federal Republic of Germany, fully known as the Act on the placing on the market, take-back and environmentally sound disposal of batteries and accumulators, is an essential set of rules that governs the handling of batteries and accumulators from their production to disposal. It was established to minimize the share of waste batteries and accumulators in waste disposal and to enhance resource efficiency through reuse and recycling.
The BattG pursues several objectives, including:
- Minimizing the environmental impacts of waste batteries and accumulators, especially regarding the hazardous substances they contain.
- Promoting the reuse and recycling of waste batteries and accumulators to reduce waste generation.
- Ensuring a high level of protection for human health and the environment throughout the life cycle of batteries and accumulators.
1.2 Historical Context and Legal Basis
The BattG was first enacted in December 2009 and has since undergone several changes and adaptations to adjust it to new technological and market-related developments. It implements various EU directives, especially the Battery Directive (2006/66/EC), into national law, thereby establishing the legal framework for handling batteries and accumulators in Germany.
The Battery Directive was issued to minimize the negative environmental impacts of waste batteries and accumulators and to harmonize the collection, treatment, recycling, and disposal of waste batteries and accumulators across the EU. It sets minimum targets for the collection of waste batteries and accumulators and their treatment, reuse, and recycling and obliges member states to take appropriate measures to achieve these targets.
The BattG sets specific requirements and obligations for manufacturers, importers, retailers, and consumers of batteries and accumulators in Germany. Among other things, it regulates the registration of manufacturers, labeling of batteries and accumulators, provision of information, collection and disposal of waste batteries and accumulators, and reporting and monitoring.
2. Who is affected by the BattG?
2.1 Manufacturers
The Battery Act (BattG) defines manufacturers as all persons who commercially place batteries or battery-powered products on the market under their own name or brand in Germany. This also includes persons who import batteries or battery-powered products from other countries to Germany. Thus, not only producers in the classic sense are affected but also importers who bring products from abroad to the German market.
2.2 Online Retailers
Online retailers and distance sellers, who sell batteries or battery-powered products directly to end-users in Germany, also fall under the definition of the manufacturer in the BattG. They must ensure that the products they distribute comply with the requirements of the BattG and fulfill their obligations regarding registration, take-back, and reporting.
2.3 Importers and Distributors
Importers, who bring batteries or battery-powered products from abroad to Germany, and distributors, who distribute these products on the German market, are also considered manufacturers within the meaning of the BattG. They must ensure that all products they place on the market in Germany comply with legal requirements and fulfill their obligations under the BattG.
2.4 B2B and B2C Sector
The BattG does not differentiate between actors in the B2B (Business-to-Business) or B2C (Business-to-Consumer) sector. Regardless of whether the products are sold to end consumers or other companies, manufacturers, importers, and retailers must observe and implement the specifications of the BattG.
3. Obligations under the BattG
3.1 Registration Obligation
Before manufacturers, importers, or retailers place batteries and accumulators on the German market, they must register with the Stiftung ear. This registration serves to ensure the take-back and recycling of batteries and includes information such as the name, address, and contact details of the manufacturer, as well as a description of the batteries placed on the market.
3.2 Reporting and Registration Obligations
Manufacturers are obliged to regularly transmit data on the quantity of batteries they have placed on the market to the disposal companies. This data is used to monitor the effectiveness of the Battery Act and to ensure that the set recycling targets are achieved.
4. Authorized Representative in the BattG
4.1 General Regulations
- Definition
An authorized representative is a natural or legal person based in Germany who has been authorized in writing by a manufacturer to fulfill certain obligations under the BattG on their behalf.
- Legal Position
The authorized representative assumes responsibility for complying with the manufacturer's legal obligations regarding the placing of batteries and accumulators on the German market.
4.2 Differences from the ElektroG
While the ElektroG requires foreign manufacturers to designate an authorized representative when placing electrical and electronic equipment on the German market, the BattG does not impose such an obligation.
5. Differences and Categories of Batteries in the BattG
5.1 General Categorization
Batteries and accumulators can be categorized according to various criteria, and the BattG takes these differences into account to establish specific regulations and requirements for the different types. Basically, the BattG distinguishes between:
- Device Batteries
These are intended to be used in devices. They can be both rechargeable (accumulators) and non-rechargeable (primary batteries).
- Industrial Batteries
These are used in industrial applications, in electric vehicles, or - if they are rechargeable batteries - as power storage for electrical energy from the power grid or from renewable energy sources.
- Vehicle Batteries
These are intended for the starter, lighting, and ignition of vehicles.
6. Labeling Obligations under the BattG
6.1 General Requirements
The labeling of batteries and accumulators is detailed in the BattG to ensure that consumers and users are informed about important aspects of the products and to promote correct disposal and recycling.
6.2 The Crossed-out Wheelie Bin Symbol
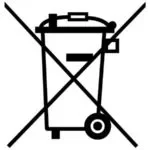
- Meaning
The crossed-out wheelie bin symbol signals that batteries and accumulators must not be disposed of with household waste.
- Application
The symbol must be affixed to all batteries, accumulators, and battery-powered devices that have been placed on the market after December 1, 2009.
- Size
The symbol must be of a certain size to ensure that it is easily recognizable.
6.3 Chemical Symbols
- Meaning
The symbols "Cd" for cadmium, "Hg" for mercury and "Pb" for lead must be displayed on batteries and accumulators containing these heavy metals.
- Application
These symbols are placed below the waste garbage can symbol if the battery or accumulator contains more than 0.002 mass percent cadmium, 0.0005 mass percent mercury or 0.004 mass percent lead.
6.4 Capacity marking
- Meaning
The capacity labeling informs the user about the electric charge of the battery or accumulator.
- Application
Since October 1, 2015, all portable and automotive batteries and accumulators must be labeled with information on electrical capacity.
- Units
The capacity must be indicated in the unit ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh) and is intended to help the user assess the performance of the battery or accumulator.
7. Take-back and Recycling Requirements under the BattG
7.1 For Manufacturers and Retailers
- Take-back of Waste Batteries
Manufacturers and retailers are obliged to take back waste batteries from end-users free of charge. This applies to batteries that they carry or have carried in their range, as well as to batteries that they use as replacements for products they distribute.
- Collection Points
Suitable collection points must be set up where consumers can return their waste batteries.
7.2 Recycling Requirements
For Manufacturers:
- Recovery
Manufacturers must ensure that the waste batteries they take back are properly recovered.
- Proof of Compliance
Manufacturers must be able to prove that the taken-back batteries have been properly recovered.
For Recycling Companies:
- Certification
Companies that recycle batteries must provide appropriate certifications to ensure that the recycling process is environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- Reporting
Recycling companies must regularly submit reports on the quantities and materials of batteries they have recycled.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.
